
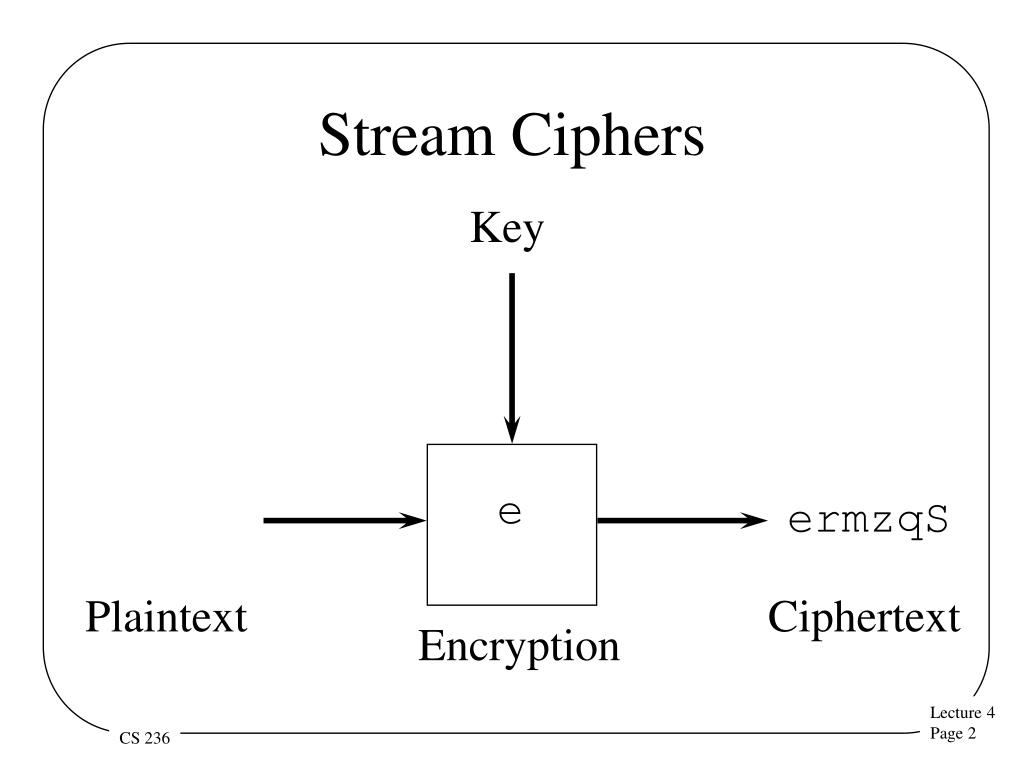
These modes fall into two categories: Confidentiality-only and Authenticated encryption with additional data modes. Several block cipher modes of operation have been developed to enable the encryption of multiple blocks of long data. On the other hand, block ciphers have a high error propagation rate since a bit of change in the original plaintext results in entirely different ciphertext blocks. This makes the encryption scheme relatively tamper-proof since it is difficult for malicious actors to insert symbols into a data block without detection. Therefore, the symmetric cipher produces a unique ciphertext block for each iteration while the IV is transmitted along with the symmetric key and does not require encryption.īlock encryption algorithms offer high diffusion that is, if a single plaintext block were subjected to multiple encryption iterations, it resulted in a unique ciphertext block for each iteration. The resultant ciphertext for the first block of characters acts as the initialization vector for the subsequent blocks. An initialization vector is a pseudorandom or random sequence of characters used to encrypt the first block of characters in the plaintext block. While Block ciphers use symmetric keys and algorithms to perform data encryption and decryption, they also require an initialization vector (IV) to function. 106 Redundant bits are added to the last block to make the entire block equal to the encryption scheme’s ciphertext block size. For instance, to perform 128-bit encryption on a 150-bit plaintext, the encryption scheme provides two blocks, 1 with 128 bits and one with the 22 bits left. If the plaintext length is not a multiple of 8, the encryption scheme uses padding to ensure complete blocks. The block size generally depends on the encryption scheme and is usually in octaves (64-bit or 128-bit blocks). What are Block Ciphers?īlock ciphers convert data in plaintext into ciphertext in fixed-size blocks. The two encryption approaches, therefore, vary widely in implementation and use cases. Let’s see the differences (short introduction)īlock ciphers encrypt data in blocks of set lengths, while stream ciphers do not and instead encrypt plaintext one byte at a time. Anyone who does not possess the secret/key cannot interpret the encrypted message. The cipher algorithms generate a truly random key cipher used only once with the one-time pad system. The encryption algorithm emulates a one-time pad system to protect the original message from unauthorized access. The sender shares the key cipher with the receiver to decrypt the message.
Symmetric cryptography (key cryptography/private key cryptography) involves using a shared key/secret to access an encoded message between two entities. However, before delving into these in detail, let us understand the basics first. stream cipher, their respective operation modes, examples, and key differences. Symmetric encryption algorithms are categorized into two: block and stream ciphers.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
